Updated: 20 March 2025 • 9 minutes Read
This is Complete Guide for Beginners in the Philippines
In today’s digital landscape, having an online presence is essential for businesses, entrepreneurs, and personal brands. Whether you are launching a corporate website, an online store, or a personal blog, the first step toward establishing your identity is to buy a domain.
But what exactly is a domain name? Why is it important? How do you choose the right one? This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about domain names, with a special focus on the Philippine market.
Table Content
- Understanding Domain Names: What They Are and How They Work
- How Domain Names Differ from URLs and Websites
- Why is a Domain Name Important?
- Types of Domains
- Difference Between Domain and Hosting
- How to Choose the Right Domain Name
- What is Domain Validity & What Happens When Your Domain Expires?
- Where to Register a Domain Name in the Philippines
- Steps to Register a Domain Name
- Domain Name Pricing: Registration, Renewal, and Transfers
Understanding Domain Names: What They Are and How They Work
A domain name is your web address, providing a unique identity for your site on the internet. Instead of requiring users to memorize complex IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.1.1), domain names provide an easy-to-remember alternative. The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses, ensuring seamless navigation online.
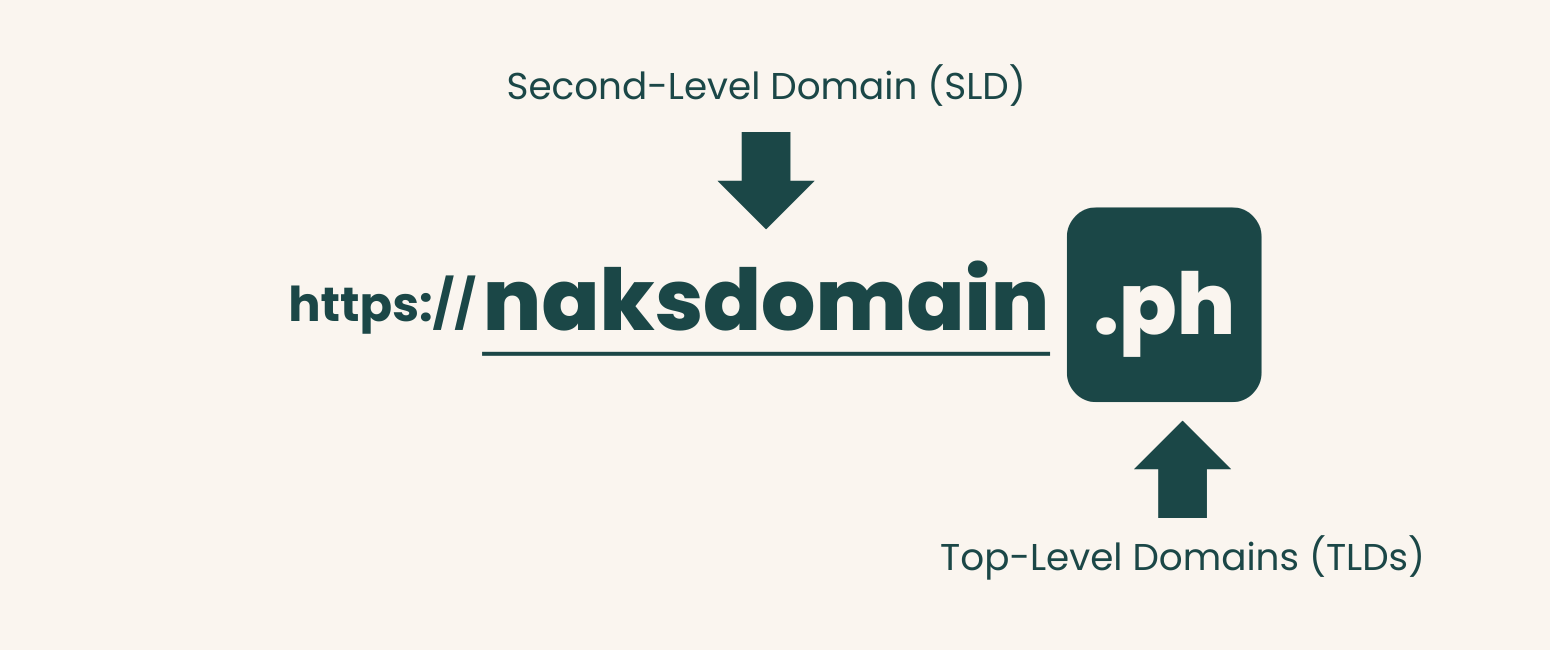
Anatomy of a Domain Name
A domain name consists of two main parts:
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the name you choose, such as “naksdomain” in ph.
- Top-Level Domains (TLDs): These are domain name extensions like .com, .net, or country-specific domain extensions such as .ph for the Philippines.
When someone enters your desired domain in a browser, the DNS directs them to the correct website server, allowing users to access your site easily.
How Domain Names Differ from URLs and Websites
Many people confuse domain names with URLs and websites. While a domain name is part of a website’s identity, it is not the same as a full website URL (which includes “https://” and additional paths).
Furthermore, having a domain name alone doesn’t mean you have a functional website—you’ll need website builders or a hosting service to create and manage content.
Why is a Domain Name Important?
A domain name is more than just an online address—it plays a crucial role in branding, credibility, and SEO. Here’s why securing the right domain name extensions is essential:
- Professionalism & Branding
A custom domain name (e.g., yourbusiness.com) enhances your brand’s credibility compared to free subdomains like yourbusiness.wordpress.com.
- SEO & Online Visibility
A keyword-rich domain name can help boost your ranking on search engines, making it easier for potential customers to find your products or services.
- Trust & Security
A domain name establishes trust with your audience. Pairing it with SSL certificates enhances security by encrypting sensitive data, especially for email addresses and transactions.
- Ownership & Control
Unlike social media pages, a registered domain name gives you full ownership and control over your online presence.
Types of Domains
There are different types of domains based on their extensions and purpose:
- Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs)
These include .com, .org, .net, .info, and .biz.
- Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs)
These are specific to countries, such as .ph (Philippines), .us (United States), and .uk (United Kingdom).
- Sponsored Top-Level Domains (sTLDs)
These are industry or community-specific domains, such as .edu (education), .gov (government), and .mil (military).
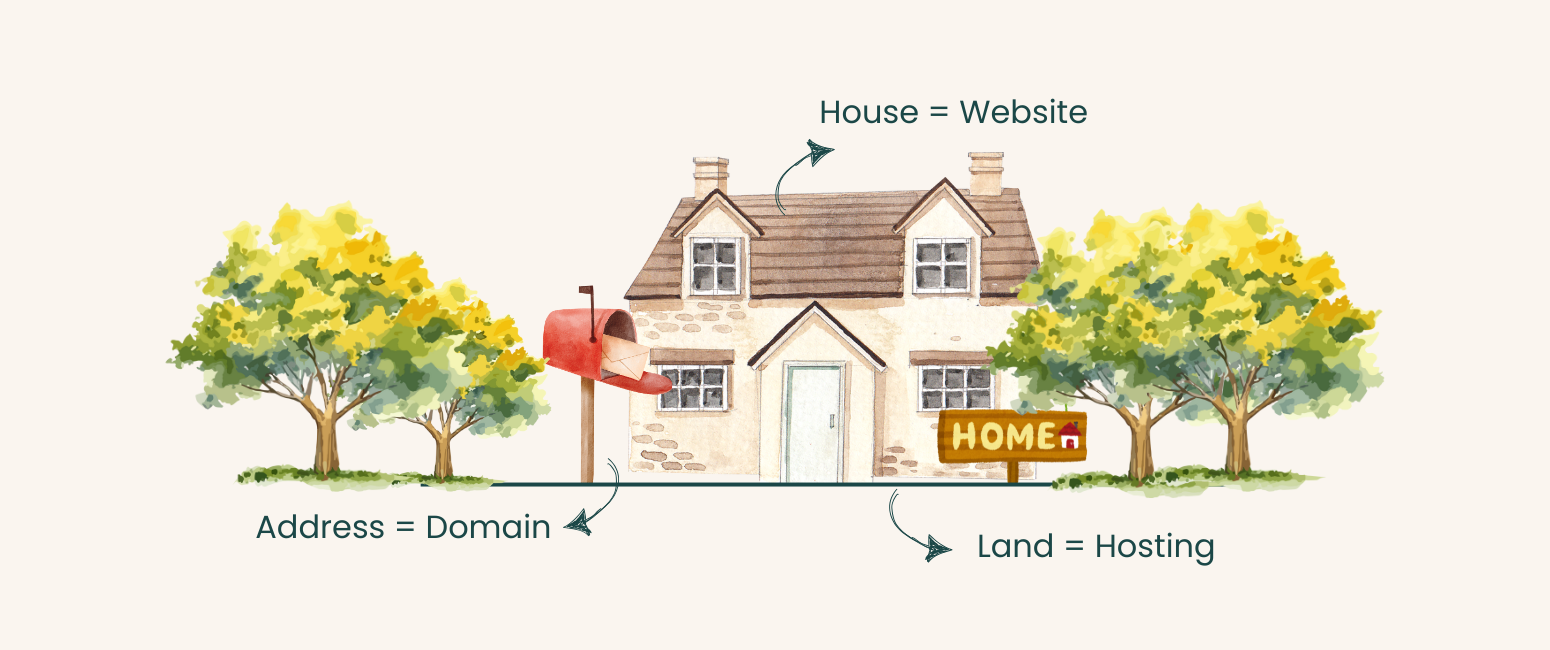
Difference Between Domain and Hosting
Many people confuse domain names with web hosting. While they work together, they serve different purposes:
- Domain Name: The web address (e.g., www.naksdomain.ph) that users type in to visit a website.
- Web Hosting: The service that stores and serves your website’s files, databases, and content so they can be accessed online. Hosting providers allocate space on a server where your website’s data is stored and managed, ensuring it is available 24/7 to users around the world.
Without hosting, a domain name would have no content to display. Conversely, without a domain, users would need to access your website using an IP address, which is not user-friendly.
How Do Domains and Hosting Work Together? Think of your website as a physical building:
- Domain Name = The Address – It guides users to your website, just like a home address directs people to your house.
- Web Hosting = The Land – It provides the storage space for your website’s files, similar to how land holds a building.
For example, if your website’s domain is www.yourwebsite.com, and you have a blog section at www.yourwebsite.com/blog, the “/blog” part acts like an apartment number, directing users to a specific section within your website.
Why You Need Both
A domain name without hosting is like an address without a house—there’s nothing to visit. Similarly, web hosting without a domain means users would need to remember a long string of numbers (IP address) to access your site, which isn’t practical.

How to Choose the Right Domain Name
Selecting the perfect domain name requires strategic planning. Here are some expert tips:
- Keep It Short and Easy to Remember
A domain name should be concise (preferably under 15 characters) and easy to remember. Avoid unnecessary hyphens and numbers.
- Use Relevant Keywords
Incorporate keywords related to your business niche. For example, an online store selling bakery items in Manila could use ManilaBakery.ph to improve local SEO.
- Choose the Right Domain Name Extensions
For businesses targeting the Philippines, top-level domains (TLDs) like .ph or .com.ph help establish a strong local presence.
- Avoid Trademark Issues
Before registering, check for trademark conflicts to prevent legal disputes. Use the Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines (IPOPHL) database for verification.
- Secure Multiple Extensions
To prevent competitors from acquiring similar names, consider purchasing variations such as .com, .ph, and .net.
- Consider Premium Domains
If your preferred desired domain is taken, explore premium domains, which are pre-registered names with high branding potential.
- Think About Future Growth
Consider how your domain will scale with your business. If you plan to expand internationally, a .com might be better than a .ph extension.

What is Domain Validity & What Happens When Your Domain Expires?
Domain Validity
A domain name is registered for a specific period, typically ranging from 1 to 10 years. During this time, the domain remains active as long as it is renewed before expiration.
What Happens When a Domain Expires?
- Grace Period: After expiration, most registrars offer a grace period (typically 30 days) where you can renew your domain without additional fees.
- Redemption Period: If not renewed, the domain enters a redemption phase (usually lasting 30-60 days), where renewal may require extra fees.
- Auction or Deletion: If still unclaimed, the domain may be auctioned to the highest bidder or released for public registration.
To avoid losing your domain, enable auto-renewal or set reminders for renewal dates.
Where to Register a Domain Name in the Philippines
Choosing a reliable domain name registrar is crucial for security, uptime, and support. Here are the top registrars serving the Philippine market:
- Affordable pricing for .ph, .com.ph and other domain extensions
- Secure services with additional offerings like web hosting, website builder and business email
- Global domain name registrar with a vast range of top-level domains (TLDs)
- Competitive first-year pricing and additional tools like website builders
- Cost-effective domain registration and renewal rates
- Free WHOIS domain privacy protection on select domain extensions
When selecting a domain name registrar, compare pricing, renewal fees, security features, and customer support to make the best decision.
Steps to Register a Domain Name
Registering a domain name is simple:
- Check Availability
Use a domain name registrar to find an available desired domain.
- Choose the Right Domain Extension
Decide between .com, .ph, or other TLDs.
- Complete Registration
Provide your contact information and finalize the payment.
- Enable Domain Privacy Protection
Protect your contact information from public WHOIS databases.
- Connect to Your Website
Link your domain name to your hosting provider and start building a website.
- Set Up Email Addresses
Many registrars offer email services linked to your domain, allowing you to create professional email addresses.

Domain Name Pricing: Registration, Renewal, and Transfers
Domain pricing varies depending on the domain extension, domain name registrar, and additional services. .ph and .com.ph domains tend to be priced higher due to their localized nature.
When choosing a domain name registrar, consider:
- Registration Fees: The initial cost to buy a domain
- Renewal Costs: Some registrars offer discounts for the first year but have higher renewal rates
- Domain Transfers: Costs associated with moving your domain name to another provider
- Additional Costs: Some registrars charge extra for features like WHOIS domain privacy protection.
Compare domain registration, renewal, and domain transfers on Naksdomain for the best deals.
Final Thoughts
A domain name is the foundation of your online presence. Choosing the right one impacts branding, SEO, and credibility. Whether you’re a business owner, freelancer, or blogger in the Philippines, securing a desired domain is the first step to building a website successfully.
By following best practices, selecting a reliable domain registrar, and understanding domain pricing, you can make an informed decision that supports your online store or website growth.
Ready to buy domains? Compare domain registration and domain transfers today at Naksdomain!
Topics: Domain
Don’t forget to share this post!


