Updated: 25 July 2023 • 14 minutes Read
A domain is necessary when building a website or creating an email address. However, many people may not have a clear understanding of the meaning of domain.
If you understand the meaning and roles of a domain, you will be able to use it more efficiently. An in-depth understanding of a domain is recommended if you plan to operate a website or own an email address.
This article will provide an easy-to-understand explanation from the basics of what a domain is to its types and how to obtain it.
|
Article table of contents
|
- What is a domain?
 The formal definition of a domain is a string of characters used to distinguish each computer connected to networks such as the Internet. In order for computers to communicate with each other on a network, they need names (hostnames) to identify themselves and be distinguished from one another.
The formal definition of a domain is a string of characters used to distinguish each computer connected to networks such as the Internet. In order for computers to communicate with each other on a network, they need names (hostnames) to identify themselves and be distinguished from one another.
The domain name is used as part of this hostname.
- host01.example.com
- host02.example.com
- host03.example.net
In the example mentioned above, the parts like “example.com” and “example.net” represent domains. An original character string such as “host01” is added to the left side of the domain name, forming the hostname that distinguishes the computers.
Hosts with the same domain name indicate they belong to the same network group.
However, it is important to note that the meaning of the domain in the context of the Internet is slightly different.
The following section explains the meaning of domains on the Internet.
A domain is like an address on the Internet.
In the Internet that we use in our daily lives, a domain name is often described as something “like an address on the Internet”. It’s important to note that it is described as ”like” an Internet address rather than stating it definitively.
In order to communicate on the Internet, it is necessary to identify ”where the other computer is located”.
In that case, it is easy to imagine the need for an “internet address”, but more accurately, the actual ”internet address” used is a series of numbers called an “IP address”. IP addresses are represented as follows.
- 192.168.100.5
- 192.168.200.10
For example, let’s say you want to see the homepage of your favourite artist. When you open the homepage on the Internet, you access the computer’s address that operates the homepage.
In the above example, “192.168.100.5” is the computer’s IP address that operates the homepage. However, if the website address you want to refer to is a list of numbers like this, it will take a lot of work for humans to remember it.
That’s where domain names come in. A domain name like “artistname.com” is relatively easy to remember. In the Internet world, a computer’s hostname and IP address using a domain is linked as follows.
www.artistname.com = 192.168.100.5
[Easy for humans to understand] = [List of numbers recognised by computers]
When referring to the homepage, suppose you enter “www.artistname.com” in the browser URL. Then, your computer or smartphone will look up the IP address from that URL (hostname). If you know the IP address, you will then be able to access the target website.
Different types of domains.
Domains are classified into multiple types depending on how they are used. To use a domain to its fullest potential, it is necessary to know the characteristics of each type. Here, we will introduce the characteristics of each major domain type.
[Original domain] An original domain is a domain that is the only one in the world.
- example.com
- example.net
To correctly distinguish computers connected to the Internet, each must have a “unique in the world” name. In the world of the Internet, it is also impossible to find the correct communication partner if multiple domains with the same name exist, just like humans have the same name.
That’s where your own domain comes into play.
For example, if a company administrator has their own domain, they can freely attach the world’s only URL to their homepage.
Taking the example of the artist homepage introduced earlier; the original domain is the “artistname.com” part. In this way, the original domain is often created with a character string, making it easy for someone else to understand “what it is used for”.
[Subdomain]
A subdomain is another domain name used to divide a single custom domain. Dividing a custom domain into subdomains makes it easier to use different domains for different purposes.
More specifically, a subdomain is a string of characters before the custom domain. Subdomains are used in the following manner.
- www.example.com
- mail.example.com
In the above example, “example.com” is the custom domain, and the parts corresponding to “www” and “mail” are the subdomains. Subdomains are expressed by separating them with a dot (.) from the custom domain.
Generally, “www” is commonly used for websites, and ”mail” is often used for mail servers. In this example, subdomains are used to differentiate between a website and a mail server, utilising the custom domain.
Without subdomains, the administrator would need to acquire a separate custom domain for each server they want to make accessible on the Internet. For instance, let’s say we have the custom domain “artist.com” and want to operate the artist’s official website and an online store separately. With subdomain names, we can differentiate and utilise the same custom domain as follows.
- Official website: www.artistname.com
- Online store: shop.artist.com
The owner of the custom domain can freely set subdomains, and they can set as many subdomains as they want.
[Top-level domain]
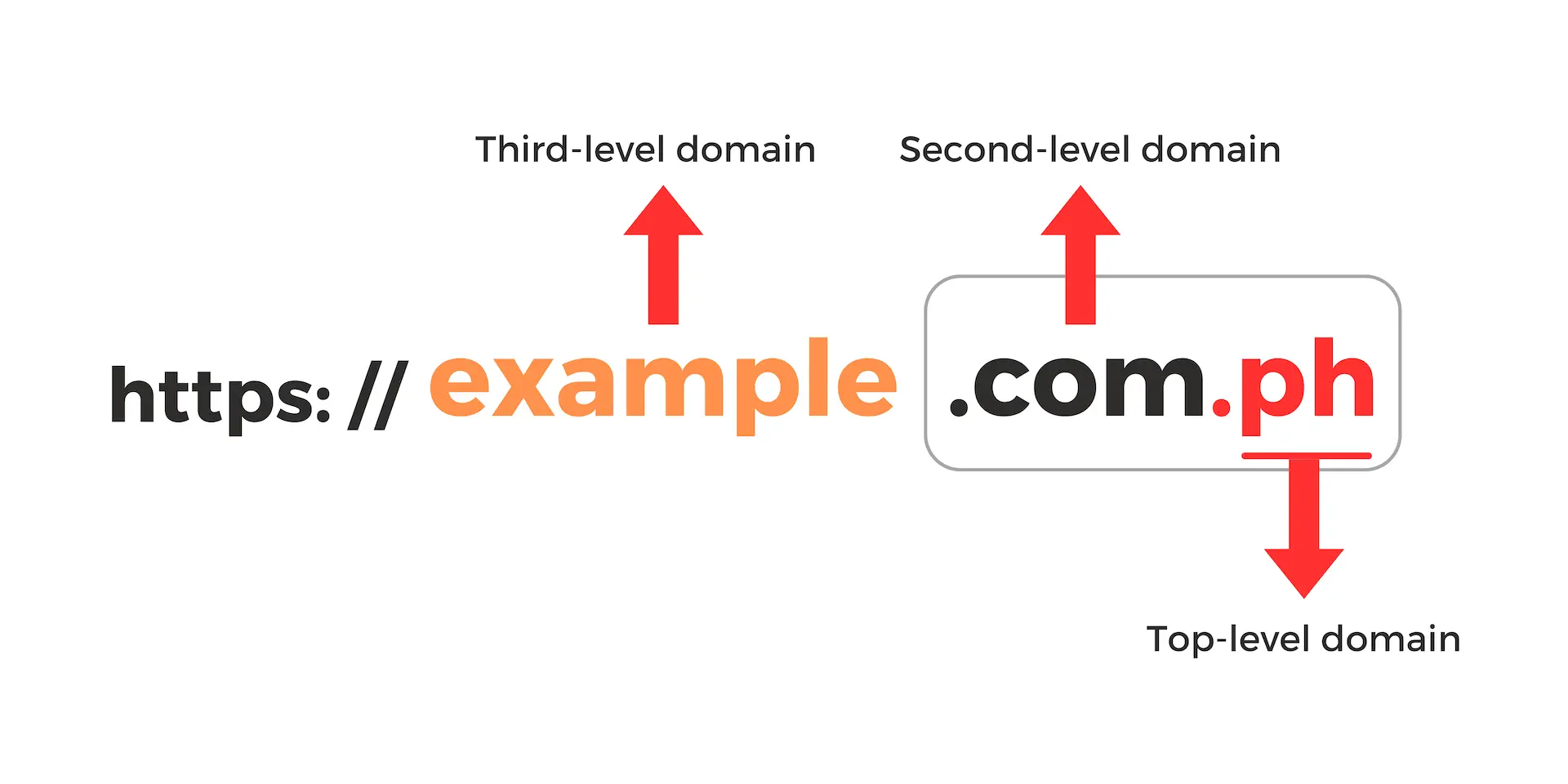 Top-level domain (TLD) refers to the rightmost part of a domain separated by a dot (.) used on the Internet. In the case of “example.com.ph”, the ”ph” portion is the top-level domain. Additionally, to the left of the top-level domain, there can be ”second-level domain” and ”third-level domain” segments separated by dots.
Top-level domain (TLD) refers to the rightmost part of a domain separated by a dot (.) used on the Internet. In the case of “example.com.ph”, the ”ph” portion is the top-level domain. Additionally, to the left of the top-level domain, there can be ”second-level domain” and ”third-level domain” segments separated by dots.
Top-level domains can be further classified based on their characteristics. When creating a domain, it is important to choose an appropriate top-level domain for it.
▼ gTLD (Generic Top-Level Domain)
gTLD domains can be acquired by individuals and companies regardless of their country or region. There is no restriction on the number of gTLD domains that can be acquired.
Types |
Uses |
.com |
Initially, it was a domain that represented commercial services.
Currently, it is widely used without specific limitations on its use. |
.net |
Initially, it was a domain that represented network services.
Currently, it is widely used without specific limitations on its use. |
.info |
Initially, it was a domain that represented information services.
Currently, it is widely used without specific limitations on its use, but it is primarily adopted for information websites. |
.org |
Initially, it was a domain that represented non-profit organisations.
Currently, it is widely used without specific limitations on its use. |
.biz |
It is a domain representing business and its use is limited to commercial purposes only. |
.mobi |
This is a domain for mobile sites.
Websites published using this domain must be optimised for mobile device viewing. |
Among the gTLD domains is a term called “new gTLD”, which refers to the types that have emerged since 2012. After this year, the evaluation criteria underwent significant changes, introducing numerous new gTLD domains. Below are some examples of these new gTLD domains.
Types |
Uses |
.academy |
Domain representing an academy or arts institution. |
.agency |
Domain indicating being an agency or representative. |
.fan |
Domain for fan sites and community websites. |
.blog |
Domain related to blogs. |
.finance |
Domain related to finance, including financial institutions and topics related to “finance, economy, and financial matters”. |
.university |
Domain representing a university. |
▼ ccTLD (Country Code Top-Level Domain)
A ccTLD is a type of top-level domain that is limited to specific countries or regions. Some examples of ccTLDs include:
For the Philippines, the “.ph” domain is available.
ccTLDs indicate the country or region associated with a website or online presence.
Types |
Uses |
.ph |
Philippines |
.sg |
Singapore |
.jp |
Japan |
.us |
United States |
“.ph” is a generic PH domain, and individuals or organisations with an address in the Philippines can register multiple domains under it.
On the other hand, the following are specific Second-Level Domains within the ”ph” domain, where a dedicated string is included, and the available organisations or services are limited. These domains are called “attribute-type PH domains”, and each organisation or service can only acquire up to one domain (individuals cannot acquire them).
Types |
Uses |
.com.ph |
Any type of companies registered in the Philippines. |
.org.ph |
Non-profit websites such as charitable organizations and educational platforms in Philippines |
.net.ph |
Activities in connection with the Internet and networks infrastructures in Philippines |
- What are the benefits of having your domain?When setting up a website or blog, it is often possible to use a domain provided by the service provider (referred to as a shared domain).A shared domain is an addition of a subdomain to the service provider’s owned domain. However, if you choose to use your own domain, you will need to go through a separate process and incur costs.
What are the advantages of obtaining your own domain? Below is a brief introduction to each of the main benefits.
It can be beneficial for SEO (search engine optimisation)
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) refers to the strategies employed to improve the ranking of a website on search engines like Google. Having your own domain can provide advantages in SEO for the following reasons.
- You can continue to use the same domain.By using the same domain for a longer period of time on your website, it can enhance the evaluation of your domain by search engines. However, if you are using a shared domain, you may need to change the domain when migrating due to service termination or other reasons.On the other hand, with your own domain, you can continue using it even when migrating services. In terms of SEO, this is more advantageous compared to a shared domain.
- Less susceptible to the influence of other users.With a shared domain, there is a possibility that the behaviour of other users using the same domain can negatively impact the evaluation of the domain by search engines. On the other hand, with your own domain, used exclusively by yourself (or your company), you are not affected by the actions of other users. Having fewer uncertain factors can be advantageous in terms of SEO.However, it should be noted that using your own domain does not guarantee a higher evaluation by search engines compared to a shared domain. It is just one factor among many that influence search results ranking. It’s important to consider other factors that also contribute to determining search result rankings.
It can be used for email addresses and more
You can use a custom domain for email addresses. By using a custom domain for your email address, you can create any desired account without the limitations of someone else already having taken the account, as is the case with free email services.
Furthermore, if you rely on free email services, there is a risk that if the service is discontinued, you will also lose access to the domain associated with your email address. However, with a custom domain, even if the email service you are using is discontinued, you can continue to use the domain for other purposes.
You can increase the credibility of your website
These days, there has been an increase in phishing sites and other fraudulent websites that mimic genuine ones. Unfortunately, it is not very difficult for malicious third parties to create fake websites.
On the other hand, by operating a website with a unique domain, you prove it is an authentic site. Visitors can then confidently browse through the website, knowing it is genuine. As a result, the credibility of the website is enhanced.
Furthermore, using a domain name related to your company, product, or brand makes it easier for visitors to remember the website’s URL. It leaves a lasting impression on visitors and ultimately contributes to building trust in the website.
- How do I get my own domain?
 The typical methods for obtaining a custom domain involve contracting it with a web hosting service or using a dedicated service for custom domains.
The typical methods for obtaining a custom domain involve contracting it with a web hosting service or using a dedicated service for custom domains.
When obtaining a custom domain in conjunction with a web hosting service, in most cases, the service provider will handle the domain configuration on your behalf. This makes it relatively easy to use a custom domain. Additionally, since the contracts are consolidated, the process becomes simpler, which is another advantage.
On the other hand, when contracting a dedicated service for custom domains, you will often need to configure the domain settings yourself. This may require more effort, but it provides you with greater flexibility in how you use the domain. For example, setting up a new website using subdomains becomes easier.
Considering these points, assessing which option aligns more closely with your preferences and is suitable for your company’s operations would be beneficial.
Regardless of the chosen method, it is important to note that you cannot apply for a domain that has already been registered. It is recommended to use a service called “whois search” to check if a domain has already been registered before proceeding with the registration process.
When it comes to domains on the Internet, they can be considered addresses that identify specific locations on the Internet. Domains come in various types, including unique “custom domains” that are one-of-a-kind worldwide and subdomains used to categorise multiple URLs under a custom domain.
Not having a custom domain doesn’t mean you can’t create a website or obtain an email address. However, as mentioned earlier, having a custom domain offers various advantages.
Considering these factors, it would be worthwhile to use a custom domain.
Topics: Domain
Don’t forget to share this post!


